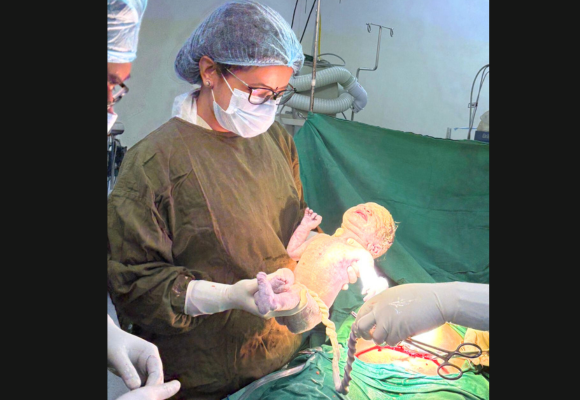
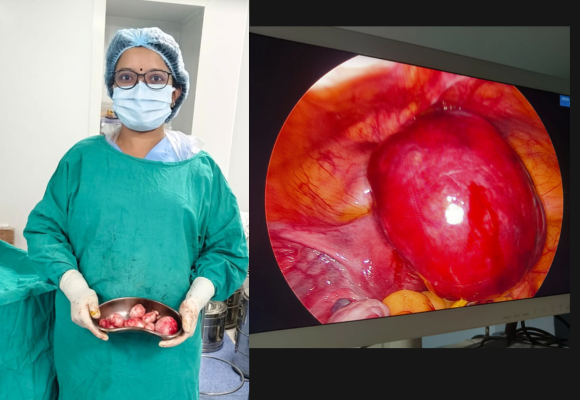
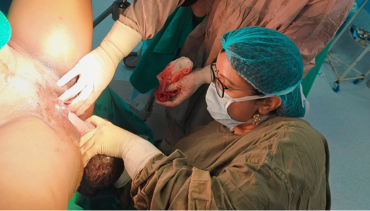
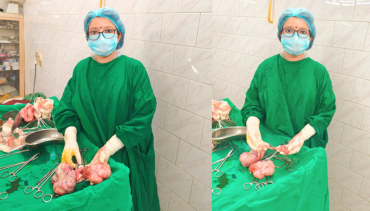
A high-risk pregnancy is a pregnancy where the mother or fetus has a higher chance of experiencing complications than in a typical pregnancy. This could be due to a number of factors, including:
Preexisting conditions:
The mother may have a chronic health condition like diabetes, high blood pressure, heart diseases, SLE
Pregnancy-related issues:
Recurrent Pregnancy loss, Obesity (increase marternal weight), IUFD (death of the fetus in womb during previous pregnancy), high blood pressure and high blood sugar in present pregnancy, Infections, Complications from a previous pregnancy, or other issues that arise during pregnancy
IVF Pregnancy: High risk pregnancy.
Age:
Pregnancies that occur before the age of 17 or after the age of 35 are considered high-risk
Multiple pregnancy:
Carrying twins or more than one fetus
Feel Safe with
Mom’s Care
Mom’s Care
Lady Obstetrician & Gynaecologist